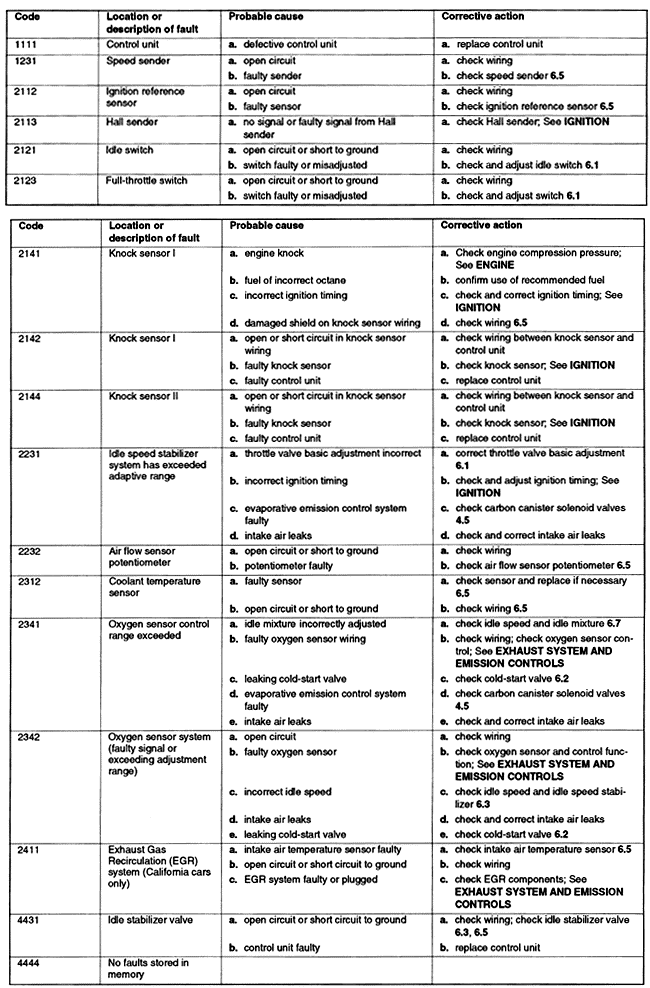
3.4 CIS-E Motronic Fault DiagnosisThe CIS-E Motronic engine management system features built-in electronic fault diagnosis which detects faults in the system during normal operation. When activated, the system displays faults as a number code which corresponds to a particular component or function of the system which should be checked. Your authorized Volkswagen dealer Service Department is equipped with an analyzer which plugs into a special diagnostic connection in the car's wiring harness. It can retrieve and interpret the fault codes, and also perform electronic checks of the differential pressure regulator, the evaporative emission control system, the idle stabilizer valve, and the cold-start valve. The analyzer and diagnostic connectors are shown in Fig. 3-1. This electronic check of the system is strongly recommended by Volkswagen as the first step in any CIS-E Motronic troubleshooting. It is most certainly recommended for any car that is still protected by Volkswagen's extensive warranty coverage. For the do-it-yourselfer, it is probably the best, most efficient way to quickly and easily diagnose a problem at a nominal cost.
System faults related to emissions or safety are stored in permanent memory and must be deliberately erased after the faults are corrected. Additional faults may be recognized by the control unit and stored in temporary memory. The temporary memory is retained whenever the ignition is switched off, but deleted the next time the engine is started.
The diagnostic connectors can also be used to activate the memory and display faults by flashing the codes on an LED test light. First make sure that fuses 15 (engine electronics), 18 (fuel pump, oxygen sensor) and 21 (interior lights) are OK, that the air conditioning is switched off, and that the engine ground strap located near the ignition distributor is intact and making a good connection. Use the procedure below to access the stored fault codes. To read stored Motronic fault codes:
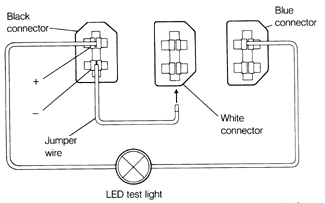
Each sequence of flashes indicates one digit of the fault code. For example, two flashes, a pause, three flashes, a pause, one flash, a pause, and two more flashes indicates the code 2-3-1-2. Table c lists the fault codes and what they mean. Table c. Motronic Diagnostic Codes
|