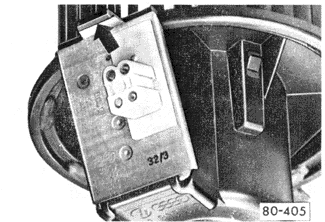
Fresh Air BlowerThe speeds of the fresh air blower motor are controlled by varying resistance. Maximum resistance produces the lowest speed. At high speed, power is supplied directly to the blower motor. On cars with air conditioning, the blower motor receives its power from the air conditioning system. Before removing a blower motor to test it, check for voltage at the blower motor harness connector with the ignition on. If there is no voltage reaching the motor, refer to the current flow diagrams for help in troubleshooting the circuit. If voltage is reaching the connector, remove the blower motor as described in BODY AND INTERIOR and check the fuses, the thermofuse, and the series resistors. For access, unclip the blower motor connecting plate as shown in Fig. 11-1.
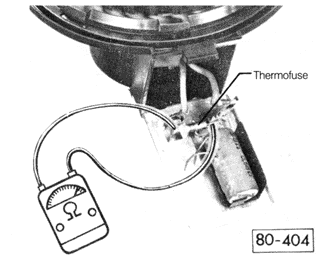
Connect an ohmmeter and check the resistance of the thermofuse as shown in Fig. 11-2. The resistance should be approximately zero. If not, the thermofuse is faulty and should be replaced.
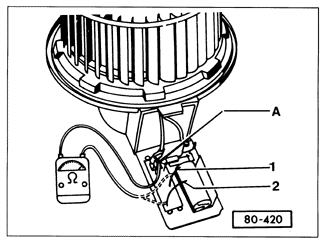
Next, test the resistors as shown in Fig. 11-3. For cars without air conditioning, the resistance ranges from 0.8 ohms (medium blower speed) to 3.3 ohms (low blower speed). There should be a similar range of three resistance values for cars with air conditioning and four blower speeds.
|