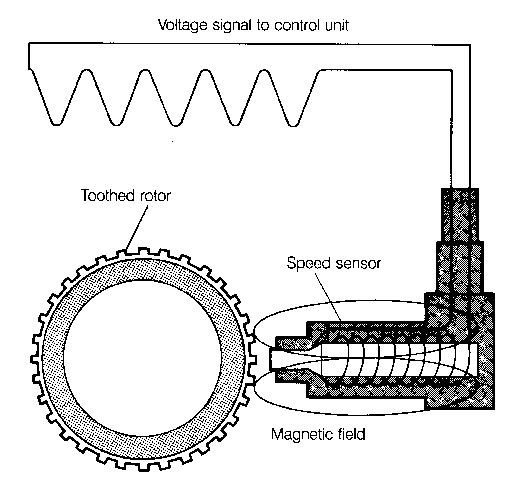
Wheel Speed SensorsThe most basic function of the ABS is to sense the very beginning of wheel lock-up so that some correction can be made to eliminate locking. The wheel speed sensors provide a signal to the control unit that represents the speed of each wheel. By evaluating the signals from the wheel speed sensors as well as comparing them to vehicle speed, the control unit can predict impending lock-up and prevent it. One wheel speed sensor is represented in Fig. 1-5. The toothed rotor at the wheel hub rotates with the wheel. The teeth of the rotor passing through the magnetic field of the sensor generate an electrical signal; the frequency of the signal changes in proportion to wheel speed. There is one speed sensor at each wheel. The toothed rotors are attached to the hubs; the sensors are mounted to the wheel bearing housings.
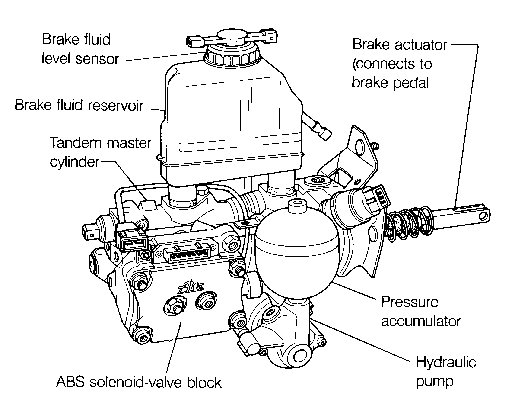
Hydraulic Modulator The hydraulic modulator is the heart of the ABS. It fulfills the functions of the standard master cylinder and brake booster, and also contains the valves which are actuated by the control unit to modulate brake pressure. The hydraulic modulator is shown in Fig. 1-6.
|