Testing Oxygen Sensor
Because of the integral nature of the fuel injection system and the oxygen sensor system, the basic measurement of fuel injection function - differential pressure regulator current - is also used to evaluate oxygen sensor performance. See FUEL SYSTEM-GASOLINE for information on measuring differential pressure regulator current.
This is a sensitive measurement. In the interest of accuracy, the engine must be fully warmed up, the exhaust system must be free of leaks, and all electrical consumers (fan, air conditioning, lights, etc.) must be off.
To test:
| 1. | Disconnect the harness connector from the differential pressure regulator. Install the test harness and connect a multimeter or ammeter for measuring differential pressure regulator current. |
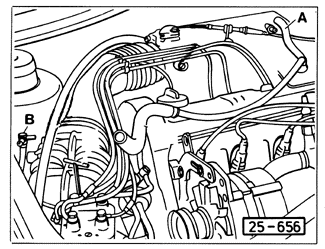
| 2. | Remove the crankcase ventilation hose from the intake manifold, as shown in Fig. 5-5, and leave it open to the atmosphere. Remove the "T" connector from the intake air boot, turn it 90°, and insert the blank side (with 1.5 mm restrictor hole) into the hole in the boot. |
| Fig. 5-5. | Crankcase ventilation hose (A) and "T" connector (B) removed for testing oxygen sensor system. "T" connector (B) is removed, turned 90°, and reinserted. See Step 2 above. |
|
| 3. | Start the engine and let it idle. After about two minutes, the meter reading should be fluctuating. If not, raise the engine speed to 3000 rpm and look again. In either case, a fluctuating current reading indicates that the oxygen sensor is operating correctly. |
| 4. | Stop the engine. Reinstall the hoses in their original configurations. Remove the test harness and reconnect the harness connector. |
No fluctuation in the meter reading (differential pressure regulator current) indicates a problem. Either the control unit, the oxygen sensor, or the wiring is faulty. To troubleshoot the system, continue testing using the procedures which follow.
|
