System Pressure and Residual PressureSystem pressure is the pressure value which is maintained in the system by the pressure regulator. When fuel pressure from the pump exceeds the desired system pressure, the regulator opens and routes fuel back to the fuel reservoir surrounding the fuel pump. System pressure is not adjustable and the pressure regulator should be replaced if it is faulty. To avoid fuel vaporization and hard starting when the engine is hot, the system is designed so that fuel pressure is retained for a time after the engine has stopped running. This residual pressure is maintained by check valves in the pressure regulator and in the fuel pump. Neither the pressure regulator check valve nor the fuel pump check valve are serviceable as individual parts. To test fuel pressure:
If the system pressure is too high, the pressure regulator is faulty and should be replaced. If the system pressure is too low, run the engine briefly to build up fuel pressure, then turn the engine off and quickly pinch shut the blue fuel return line. If the pressure holds, then the pressure regulator is faulty and should be replaced.
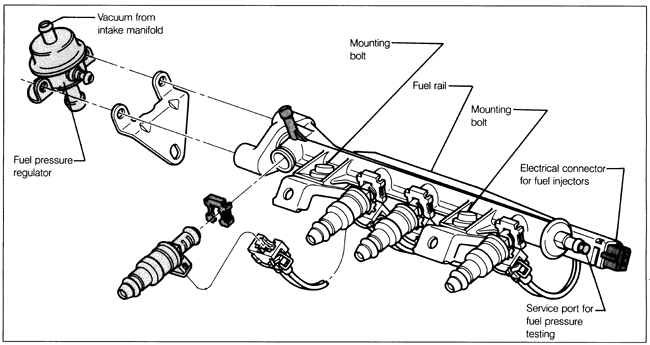
If the pressure still drops, check for leaks in the fuel system. If no leaks are found, the fault may be due to a leaky fuel injector, a faulty fuel injector O-ring, or a faulty fuel pump check valve. To conclude the fuel pressure testing, disconnect the gauge from the fuel rail service port and catch any spilling fuel with a clean rag. Install the sealing screw with a new seal. |