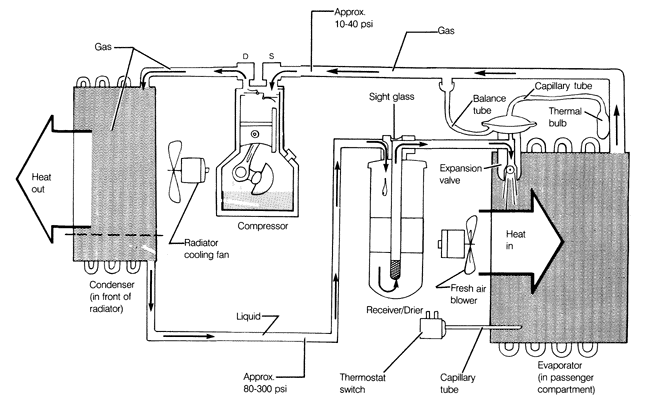
9.1 System DescriptionFig. 9-1 is a schematic view of a typical automobile air conditioning (A/C) system. The air conditioning system removes heat and moisture from the passenger compartment. It accomplishes this through the application of four principles: materials absorb heat as they change from a liguid to a gas (evaporate); materials give off heat as they change from a gas to a liquid (condense); the boiling point of a liquid varies with its pressure; and, heat always flows from hot to cold. For example, the first principle is demonstrated by wetting your hand and then blowing on it. As the water evaporates, it takes some heat with it and your hand feels cooler. In the air conditioning system, the heat from the passenger compartment boils (evaporates) the refrigerant (R-12) in the evaporator, causing the heat to be absorbed by the R-12. This heat is then released into the atmosphere when the R-12 is cooled and condensed into a liquid at the condenser. Moisture is removed at the evaporator in the same way that water drops form on a cold glass. The moisture drips onto the water tray beneath the evaporator (located behind the dash) and is routed outside. This is the reason a water puddle may often be seen under the car when the A/C is operating. The compressor forces the R-12 through the system and at the same time pressurizes the R-12, raising its boiling point to make it more easily condensed. The compressor is engaged by an electro-magnetic clutch which is actuated when the A/C is turned on. The thermostat switch automatically disengages the clutch when the temperature in the passenger compartment reaches the level set on the operating controls. The condenser, which looks like a small radiator, is located in front of the engine radiator. The receiver/drier removes small amounts of moisture and dirt from the system. The expansion valve maintains a steady temperature in the system by metering the flow of R-12 based on the temperature of the refrigerant as it leaves the evaporator.
|